Oral Cancer/মুখের ক্যান্সার
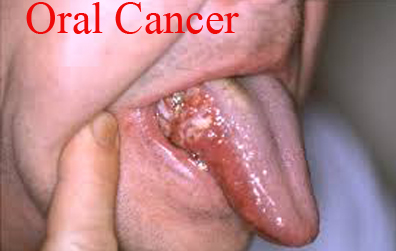
Dangerous Oral Cancer. Mobile Phone Number 01797522136. Oral cancer is cancer forming in the tissues of the mouth or the back of the throat, primarily caused by tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. Key clinical features include sores or white/red patches in the mouth that don’t heal, lumps, difficulty swallowing, and neck swelling. Early detection through regular dental visits is crucial for successful treatment.
HRTD Medical Institute ( An Organization of HRTD Limited Which is Registered by the Govt of the People Republic of Bangladesh) has been working in Medical and Dental Sector science January 2014. We provide some Medical and Dental Courses for the assistance of Doctors in their working field like Hospital, Clinic, Diagnostic Center, Caregiver Center, Community Clinic, Doctors Chamber, Dental Chambers, Health Centers of Schools, Colleges, Universities and NGOs. These Medical and Dental Assistant Courses are Paramedical Courses, Diploma Medical Assistant Course, Diploma in Medicine and Surgery Course, DMDS Course, DPM Course, Nursing Course, Nursing Assistant Diploma Course, Caregiving Course, Pathology Course, Physiotherapy Course, Dental Short Courses and Diploma Dental Courses, etc. All these courses are available in HRTD Medical Institute.
Definition of Oral Cancer/ মুখের ক্যান্সার
Oral cancer, or mouth cancer, is a type of head and neck cancer that develops in the lips, tongue, gums, inner lining of the cheeks, roof and floor of the mouth, or the throat at the back of the mouth. It arises from mutations in the DNA of the flat, thin squamous cells that line these areas, leading to abnormal, uncontrolled cell growth that forms a tumor.
Causes of Oral Cancer
The primary risk factors for oral cancer include:
- Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and using smokeless tobacco products like chewing tobacco and snuff are major causes.
- Excessive alcohol intake: Drinking too much alcohol significantly increases the risk.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): A specific type of HPV is linked to oropharyngeal cancers, which affect the back of the tongue, tonsils, and throat.
- Sun exposure: Prolonged, excessive sun exposure can cause lip cancers.
- Genetics: A family history of cancer can increase risk.
- Other factors: Poor oral hygiene, a weakened immune system, certain dietary deficiencies, and the use of betel quid (a chewing stimulant common in Asia) are also associated with an increased risk.
Clinical Features of Oral Cancer/মুখের ক্যান্সার
Symptoms and signs of oral cancer can be subtle in the early stages and may include:
- Mouth sores: A mouth ulcer or sore that doesn’t heal within a few weeks.
- White or red patches: Patches of red or white in the mouth that may be painless.
- Lumps: A lump on the lip, inside the mouth, or in the neck.
- Pain: Persistent mouth pain or pain in the throat.
- Difficulty with function: Numbness in the mouth, trouble swallowing (dysphagia), changes in voice, or a loose tooth.
- Other signs: Unexplained weight loss and bleeding in the mouth can also occur.
It is essential to see a doctor or dentist for any symptom that lasts more than two weeks.
মুখের ক্যান্সার হলো মুখের টিস্যুতে বা গলার পিছনের অংশে তৈরি ক্যান্সার, যা মূলত তামাক ব্যবহার, অতিরিক্ত অ্যালকোহল সেবন এবং হিউম্যান প্যাপিলোমাভাইরাস (HPV) সংক্রমণের কারণে ঘটে। মুখের মূল ক্লিনিকাল বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে মুখে ঘা বা সাদা/লাল দাগ যা সেরে যায় না, পিণ্ড, গিলতে অসুবিধা এবং ঘাড় ফুলে যাওয়া। সফল চিকিৎসার জন্য নিয়মিত দাঁতের ডাক্তারের কাছে যাওয়ার মাধ্যমে প্রাথমিক পর্যায়ে রোগ নির্ণয় অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
সংজ্ঞা
মুখের ক্যান্সার, বা মুখের ক্যান্সার, হল এক ধরণের মাথা এবং ঘাড়ের ক্যান্সার যা ঠোঁট, জিহ্বা, মাড়ি, গালের ভেতরের আস্তরণ, মুখের ছাদ এবং মেঝে, অথবা মুখের পিছনের গলায় বিকশিত হয়। এটি এই অঞ্চলগুলিকে রেখাযুক্ত সমতল, পাতলা স্কোয়ামাস কোষের ডিএনএ-তে মিউটেশনের ফলে উদ্ভূত হয় , যার ফলে অস্বাভাবিক, অনিয়ন্ত্রিত কোষ বৃদ্ধি ঘটে যা একটি টিউমার তৈরি করে।
কারণসমূহ
মুখের ক্যান্সারের প্রাথমিক ঝুঁকির কারণগুলির মধ্যে রয়েছে:
- তামাক ব্যবহার: সিগারেট, সিগার, পাইপ ধূমপান এবং ধোঁয়াবিহীন তামাকজাত দ্রব্য যেমন চিবানো তামাক এবং নাস ব্যবহার করা এর প্রধান কারণ।
- অতিরিক্ত অ্যালকোহল গ্রহণ: অতিরিক্ত অ্যালকোহল পান ঝুঁকি উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে বৃদ্ধি করে।
- হিউম্যান প্যাপিলোমাভাইরাস (HPV): একটি নির্দিষ্ট ধরণের এইচপিভি অরোফ্যারিঞ্জিয়াল ক্যান্সারেরসাথে যুক্ত , যা জিহ্বার পিছনের অংশ, টনসিল এবং গলাকে প্রভাবিত করে।
- সূর্যের আলো: দীর্ঘক্ষণ, অতিরিক্ত সূর্যের আলোয় থাকার ফলে ঠোঁটের ক্যান্সার হতে পারে।
- জেনেটিক্স: ক্যান্সারের পারিবারিক ইতিহাস ঝুঁকি বাড়াতে পারে।
- অন্যান্য কারণ: দুর্বল মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যবিধি, দুর্বল রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা, কিছু খাদ্যতালিকাগত ঘাটতি এবং সুপারি (এশিয়ায় প্রচলিত একটি চিবানো উদ্দীপক) ব্যবহারও ঝুঁকি বৃদ্ধির সাথে যুক্ত।
ক্লিনিকাল বৈশিষ্ট্য
প্রাথমিক পর্যায়ে মুখের ক্যান্সারের লক্ষণ ও লক্ষণগুলি সূক্ষ্ম হতে পারে এবং এর মধ্যে অন্তর্ভুক্ত থাকতে পারে:
- মুখের ঘা: মুখের আলসার বা ঘা যা কয়েক সপ্তাহের মধ্যে সেরে না।
- সাদা বা লাল দাগ: মুখে লাল বা সাদা দাগ যা ব্যথাহীন হতে পারে।
- পিণ্ড: ঠোঁটে, মুখের ভেতরে, অথবা ঘাড়ে একটি পিণ্ড।
- ব্যথা: মুখে ক্রমাগত ব্যথা বা গলায় ব্যথা।
- কার্যকারিতার অসুবিধা: মুখের অসাড়তা, গিলতে সমস্যা (ডিসফ্যাজিয়া), কণ্ঠস্বরের পরিবর্তন, অথবা দাঁত আলগা হয়ে যাওয়া।
- অন্যান্য লক্ষণ: অব্যক্ত ওজন হ্রাস এবং মুখে রক্তপাতও ঘটতে পারে।
দুই সপ্তাহের বেশি সময় ধরে যে কোনও লক্ষণ দেখা দিলে ডাক্তার বা দন্তচিকিৎসকের সাথে দেখা করা অপরিহার্য।
How tobacco causes Oral Cancer?
Some of the chemicals contained in tobacco smoke and chewing tobacco are carcinogenic, meaning they can cause genetic changes in cells of the mouth cavity, leading to the development of oral cancer.
তামাকের ধোঁয়া এবং চিবানো তামাকের মধ্যে থাকা কিছু রাসায়নিক পদার্থ কার্সিনোজেনিক, যার অর্থ তারা মুখের গহ্বরের কোষগুলিতে জিনগত পরিবর্তন ঘটাতে পারে, যার ফলে মুখের ক্যান্সারের বিকাশ ঘটে।
How Excessive Alcohol Drinking causes Oral Cancer?
Alcohol works in the following ways: Dries out the skin of the mouth and makes it more porous. It is broken down by bacteria in the mouth to make cancer-causing chemicals. Breaks down within the body to produce chemicals which are poisonous to cells and damage their DNA.
অ্যালকোহল নিম্নলিখিত উপায়ে কাজ করে: মুখের ত্বক শুষ্ক করে এবং এটিকে আরও ছিদ্রযুক্ত করে তোলে। এটি মুখের ব্যাকটেরিয়া দ্বারা ভেঙে ক্যান্সার সৃষ্টিকারী রাসায়নিক তৈরি করে। শরীরের অভ্যন্তরে ভেঙে এমন রাসায়নিক তৈরি করে যা কোষের জন্য বিষাক্ত এবং তাদের ডিএনএ ক্ষতি করে।
How Human Papillomavirus causes cancer?
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) causes cancer by integrating its DNA into host cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and division. High-risk HPV types can persist in the body, changing cell DNA and creating precancerous cells that can eventually become cancerous over many years. Factors like smoking or a weakened immune system can increase the risk of a persistent, cancer-causing HPV infection.
How HPV Causes Cancer
- Cellular Interference: High-risk HPV types infect skin cells, particularly in the genital area, and interfere with the normal functioning of the cell’s DNA.
- Uncontrolled Cell Division: The virus alters the cell’s DNA to promote uncontrolled cell multiplication and growth, rather than normal cell replication and communication.
- Persistent Infection: While the immune system clears most HPV infections, high-risk types can persist, allowing these abnormal, rapidly dividing cells to form precancerous lesions.
- Cancer Development: Over time, these precancerous cells can accumulate further genetic changes, lose normal cell control, and develop into cancer, a process that can take years or even decades.
Risk Factors
- Persistence: An infection that the body does not clear.
- Aggressive HPV Types: Certain high-risk types, such as HPV 16 and 18, are more likely to cause cancer.
- Weakened Immune System: A compromised immune system, such as from HIV or immunosuppressive medications, increases the risk of a lasting infection.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can increase the risk of HPV-related cancers.
Prevention
- HPV Vaccine: The HPV vaccine can prevent most HPV-related cancers by protecting against the high-risk HPV types that cause them.
- Screening: For cervical cancer, regular Pap tests or HPV tests can detect precancerous cells before they become cancerous.
হিউম্যান প্যাপিলোমাভাইরাস (HPV) তার ডিএনএকে হোস্ট কোষের সাথে একীভূত করে ক্যান্সার সৃষ্টি করে, যার ফলে কোষের অনিয়ন্ত্রিত বৃদ্ধি এবং বিভাজন ঘটে। উচ্চ-ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ এইচপিভি প্রকারগুলি শরীরে টিকে থাকতে পারে, কোষের ডিএনএ পরিবর্তন করে এবং প্রাক-ক্যান্সারাস কোষ তৈরি করে যা অবশেষে বহু বছর ধরে ক্যান্সারে পরিণত হতে পারে। ধূমপান বা দুর্বল রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতার মতো কারণগুলি ক্রমাগত ক্যান্সার সৃষ্টিকারী এইচপিভি সংক্রমণের ঝুঁকি বাড়িয়ে তুলতে পারে।
এইচপিভি কীভাবে ক্যান্সারের কারণ হয়
- কোষীয় হস্তক্ষেপ: উচ্চ-ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ এইচপিভি প্রকারগুলি ত্বকের কোষগুলিকে সংক্রামিত করে, বিশেষ করে যৌনাঙ্গের অঞ্চলে, এবং কোষের ডিএনএর স্বাভাবিক কার্যকারিতায় হস্তক্ষেপ করে।
- অনিয়ন্ত্রিত কোষ বিভাজন: ভাইরাসটি স্বাভাবিক কোষের প্রতিলিপি এবং যোগাযোগের পরিবর্তে, অনিয়ন্ত্রিত কোষের সংখ্যাবৃদ্ধি এবং বৃদ্ধিকে উৎসাহিত করার জন্য কোষের ডিএনএ পরিবর্তন করে।
- স্থায়ী সংক্রমণ: যদিও রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থা বেশিরভাগ এইচপিভি সংক্রমণ পরিষ্কার করে, উচ্চ-ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ প্রকারগুলি টিকে থাকতে পারে, যার ফলে এই অস্বাভাবিক, দ্রুত বিভাজিত কোষগুলি প্রাক-ক্যান্সারজনিত ক্ষত তৈরি করতে পারে।
- ক্যান্সারের বিকাশ: সময়ের সাথে সাথে, এই প্রাক-ক্যান্সারাস কোষগুলি আরও জিনগত পরিবর্তন জমা করতে পারে, স্বাভাবিক কোষ নিয়ন্ত্রণ হারাতে পারে এবং ক্যান্সারে পরিণত হতে পারে, একটি প্রক্রিয়া যা বছরের পর বছর এমনকি দশক ধরেও সময় নিতে পারে।
ঝুঁকির কারণ
- অধ্যবসায়: এমন একটি সংক্রমণ যা শরীর পরিষ্কার করতে পারে না।
- আক্রমণাত্মক এইচপিভি প্রকার: কিছু উচ্চ-ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ প্রকার, যেমন HPV 16 এবং 18, ক্যান্সার সৃষ্টির সম্ভাবনা বেশি।
- দুর্বল রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা: এইচআইভি বা ইমিউনোসপ্রেসিভ ওষুধের মতো দুর্বল রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা দীর্ঘস্থায়ী সংক্রমণের ঝুঁকি বাড়ায়।
- ধূমপান: তামাক ব্যবহার HPV-সম্পর্কিত ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি বাড়াতে পারে।
প্রতিরোধ
- এইচপিভি ভ্যাকসিন: এইচপিভি ভ্যাকসিন বেশিরভাগ এইচপিভি-সম্পর্কিত ক্যান্সার প্রতিরোধ করতে পারে, কারণ এটি উচ্চ-ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ এইচপিভি ধরণের ক্যান্সারের বিরুদ্ধে সুরক্ষা প্রদান করে।
- স্ক্রিনিং: জরায়ুমুখের ক্যান্সারের ক্ষেত্রে, নিয়মিত প্যাপ পরীক্ষা বা এইচপিভি পরীক্ষা ক্যান্সারে পরিণত হওয়ার আগে প্রাক-ক্যান্সারাস কোষ সনাক্ত করতে পারে।
How Sun exposure causes Oral Cancer?
Sun exposure causes lip cancer, a form of oral cancer, by exposing the lips’ squamous cells to damaging UV radiation, which leads to DNA mutations that can cause cancerous growth. This effect is cumulative over time, and prolonged sun exposure can lead to a precancerous condition called actinic cheilitis before developing into squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
How UV Radiation Causes Damage
- DNA Damage: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun damages the DNA in the cells of your lips.
- Mutations: This damage can cause mutations in the cells’ DNA, leading to abnormal cell growth.
- Actinic Cheilitis: Over time, this damage can manifest as a precancerous condition where the lips become dry, scaly, and discolored, known as actinic cheilitis.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Continued exposure can then lead to squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), the most common type of lip cancer.
Risk Factors & Cumulative Exposure
- Cumulative Effect: The risk increases with age because sun damage is cumulative, meaning repeated exposure over many years builds up.
- Work and Lifestyle: Individuals who work outdoors or spend many hours in the sun daily are at a higher risk.
Prevention Measures
- SPF Lip Balm: Use lip balms with a high sun protection factor (SPF) to protect your lips.
- Sun Safety: Follow safe sun practices, like wearing a wide-brimmed hat or seeking shade during peak sun hours (around 10 a.m. to 2 p.m.).
- Regular Check-ups: Get regular oral cancer screenings from a dentist to detect any early signs of the disease.
সূর্যের সংস্পর্শে ঠোঁটের ক্যান্সার হয়, যা মুখের ক্যান্সারের একটি রূপ, কারণ ঠোঁটের স্কোয়ামাস কোষগুলি ক্ষতিকারক UV বিকিরণের সংস্পর্শে আসে, যা DNA মিউটেশনের দিকে পরিচালিত করে যা ক্যান্সারের বৃদ্ধি ঘটাতে পারে। এই প্রভাব সময়ের সাথে সাথে ক্রমবর্ধমান হয় এবং দীর্ঘক্ষণ সূর্যের আলোতে থাকার ফলে অ্যাক্টিনিক চাইলাইটিস নামক একটি প্রাক-ক্যান্সারজনিত অবস্থা দেখা দিতে পারে যা স্কোয়ামাস সেল কার্সিনোমা (SCC)তে পরিণত হওয়ার আগে ঘটে ।
কিভাবে UV বিকিরণ ক্ষতি করে
- ডিএনএ ক্ষতি: সূর্যের অতিবেগুনী (UV) বিকিরণ আপনার ঠোঁটের কোষের DNA-এর ক্ষতি করে।
- মিউটেশন: এই ক্ষতি কোষের ডিএনএতে মিউটেশন ঘটাতে পারে, যার ফলে অস্বাভাবিক কোষ বৃদ্ধি ঘটে।
- অ্যাক্টিনিক চাইলাইটিস: সময়ের সাথে সাথে, এই ক্ষতি একটি প্রাক-ক্যান্সার অবস্থা হিসাবে প্রকাশ পেতে পারে যেখানে ঠোঁট শুষ্ক, খসখসে এবং বিবর্ণ হয়ে যায়, যা অ্যাক্টিনিক চাইলাইটিস নামে পরিচিত।
- স্কোয়ামাস সেল কার্সিনোমা: ক্রমাগত সংস্পর্শে আসার ফলে স্কোয়ামাস সেল কার্সিনোমা (SCC) হতে পারে, যা ঠোঁটের ক্যান্সারের সবচেয়ে সাধারণ ধরণ।
ঝুঁকির কারণ এবং ক্রমবর্ধমান এক্সপোজার
- ক্রমবর্ধমান প্রভাব: বয়স বাড়ার সাথে সাথে ঝুঁকি বৃদ্ধি পায় কারণ সূর্যের ক্ষতি ক্রমবর্ধমান হয়, যার অর্থ বহু বছর ধরে বারবার সূর্যের সংস্পর্শে আসার ফলে ক্ষতি বৃদ্ধি পায়।
- কাজ এবং জীবনধারা: যারা বাইরে কাজ করেন বা প্রতিদিন অনেক ঘন্টা রোদে কাটান তাদের ঝুঁকি বেশি।
প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থা
- এসপিএফ লিপ বাম: আপনার ঠোঁটকে সুরক্ষিত রাখতে উচ্চ সূর্য সুরক্ষা ফ্যাক্টর (SPF) সহ লিপ বাম ব্যবহার করুন।
- সূর্য সুরক্ষা: নিরাপদ রোদের অভ্যাসগুলি অনুসরণ করুন, যেমন চওড়া কাঁটাওয়ালা টুপি পরা অথবা রোদের সর্বোচ্চ সময়ে (সকাল ১০টা থেকে দুপুর ২টার দিকে) ছায়া খোঁজা।
- নিয়মিত চেক-আপ: রোগের প্রাথমিক লক্ষণ সনাক্ত করার জন্য নিয়মিত দাঁতের ডাক্তারের কাছ থেকে মুখের ক্যান্সারের স্ক্রিনিং করান।
How Poor oral hygiene can cause Oral Cancer?
Poor oral hygiene contributes to oral cancer risk by fostering chronic inflammation, enabling bacteria and viruses (like HPV) to thrive, and weakening the mouth’s ability to fight abnormal cell growth. This persistent irritation and compromised immune response can lead to cell mutations and the development of oral cancer over time.
Mechanisms of Poor Oral Hygiene Leading to Oral Cancer
- Chronic Inflammation: Neglecting oral hygiene leads to the buildup of plaque and tartar, which cause chronic inflammation of the gums and oral tissues. This persistent inflammation can create an environment where cells are more likely to mutate and become cancerous.
- Increased Bacteria and Viral Load: Poor oral hygiene creates a breeding ground for harmful bacteria and viruses, such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV), which is a known cause of many mouth cancers. A cleaner mouth helps keep these pathogens in check.
- Weakened Immune Response: Chronic infections and inflammation from poor oral health place a continuous burden on the immune system. This makes it harder for the body to detect and destroy abnormal cells before they develop into cancer.
- Reduced Tissue Defense: Poor oral health can weaken the mouth’s natural defenses, making oral tissues more vulnerable to damage and the harmful effects of other carcinogens from substances like tobacco and alcohol.
How to Prevent Oral Cancer through Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush and Floss Daily: Regular brushing and flossing remove plaque and bacteria, reducing inflammation and gum disease.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Professional cleanings and exams by a dentist can detect dental problems early and prevent them from escalating into more serious conditions, including precancerous changes.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: While not a direct hygiene measure, a healthy diet and lifestyle support a strong immune system, which is crucial for fighting off abnormal cell growth.
দুর্বল মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যবিধি দীর্ঘস্থায়ী প্রদাহ বৃদ্ধি করে, ব্যাকটেরিয়া এবং ভাইরাস (যেমন HPV) বৃদ্ধি পেতে সক্ষম করে এবং অস্বাভাবিক কোষ বৃদ্ধির বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করার মুখের ক্ষমতাকে দুর্বল করেমুখের ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি বাড়ায় । এই ক্রমাগত জ্বালা এবং রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা হ্রাসের ফলে কোষের পরিবর্তন হতে পারে এবং সময়ের সাথে সাথে মুখের ক্যান্সারের বিকাশ ঘটতে পারে।
দুর্বল মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যবিধির প্রক্রিয়াগুলি মৌখিক ক্যান্সারের দিকে পরিচালিত করে
- দীর্ঘস্থায়ী প্রদাহ: মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যবিধি অবহেলা করলে প্লাক এবং টার্টার তৈরি হয়, যা মাড়ি এবং মৌখিক টিস্যুতে দীর্ঘস্থায়ী প্রদাহ সৃষ্টি করে। এই ক্রমাগত প্রদাহ এমন একটি পরিবেশ তৈরি করতে পারে যেখানে কোষগুলির পরিবর্তন এবং ক্যান্সারে পরিণত হওয়ার সম্ভাবনা বেশি থাকে।
- ব্যাকটেরিয়া এবং ভাইরাল লোড বৃদ্ধি: দুর্বল মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যবিধি ক্ষতিকারক ব্যাকটেরিয়া এবং ভাইরাসের প্রজনন ক্ষেত্র তৈরি করে, যেমন হিউম্যান প্যাপিলোমাভাইরাস (HPV), যা অনেক মুখের ক্যান্সারের একটি পরিচিত কারণ। পরিষ্কার মুখ এই রোগজীবাণুগুলিকে নিয়ন্ত্রণে রাখতে সাহায্য করে।
- দুর্বল রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা: দুর্বল মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্যের কারণে দীর্ঘস্থায়ী সংক্রমণ এবং প্রদাহ রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থার উপর ক্রমাগত বোঝা চাপিয়ে দেয়। এর ফলে শরীরের পক্ষে অস্বাভাবিক কোষগুলি ক্যান্সারে পরিণত হওয়ার আগে সনাক্ত করা এবং ধ্বংস করা কঠিন হয়ে পড়ে।
- টিস্যু প্রতিরক্ষা হ্রাস: দুর্বল মৌখিক স্বাস্থ্য মুখের প্রাকৃতিক প্রতিরক্ষাকে দুর্বল করে দিতে পারে, যার ফলে মুখের টিস্যুগুলি ক্ষতির জন্য এবং তামাক এবং অ্যালকোহলের মতো পদার্থ থেকে অন্যান্য কার্সিনোজেনের ক্ষতিকারক প্রভাবের জন্য আরও ঝুঁকিপূর্ণ হয়ে ওঠে।
ভালো মুখের স্বাস্থ্যবিধির মাধ্যমে মুখের ক্যান্সার কীভাবে প্রতিরোধ করা যায়
- প্রতিদিন ব্রাশ এবং ফ্লস করুন: নিয়মিত ব্রাশিং এবং ফ্লসিং প্লাক এবং ব্যাকটেরিয়া দূর করে, প্রদাহ এবং মাড়ির রোগ কমায়।
- নিয়মিত দাঁতের পরীক্ষা: একজন দন্তচিকিৎসকের দ্বারা পেশাদার পরিষ্কার এবং পরীক্ষা দাঁতের সমস্যাগুলি প্রাথমিক পর্যায়ে সনাক্ত করতে পারে এবং এগুলিকে আরও গুরুতর অবস্থার দিকে ঠেকাতে পারে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে প্রাক-ক্যান্সারজনিত পরিবর্তন।
- স্বাস্থ্যকর জীবনধারা বজায় রাখুন: যদিও এটি সরাসরি স্বাস্থ্যবিধি পরিমাপ নয়, একটি স্বাস্থ্যকর খাদ্যাভ্যাস এবং জীবনধারা একটি শক্তিশালী রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতাকে সমর্থন করে, যা অস্বাভাবিক কোষ বৃদ্ধির বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করার জন্য অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ।
Dietary deficiencies that causes oral cancer
Dietary deficiencies linked to increased oral cancer risk include insufficient intake of vitamins A, C, D, and E, and minerals such as selenium, zinc, and iron. These deficiencies can weaken the immune system, impair DNA repair, and increase oxidative stress, all of which make cells more susceptible to cancerous changes. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and dietary fiber is associated with a reduced risk of oral cancer.
Specific Deficiencies and Their Impact
- Vitamin D: Deficiency is strongly associated with higher oral cancer risk.
- Vitamins A, C, and E: These antioxidants help protect against DNA damage and neutralize free radicals.
- Iron: Low levels of iron are linked to increased oxidative stress, raising oral cancer risk.
- Selenium: Deficiency can impair the activity of antioxidant enzymes, contributing to the development of oral cancer.
- Zinc: Deficiency is linked to increased cancer risk and plays a role in cellular proliferation and immune function.
- Glutathione (GSH): Low levels are associated with increased oxidative stress and a higher risk of oral cancer.
How Deficiencies Contribute to Cancer
- Oxidative Stress: A lack of antioxidants like vitamins A, C, and E, and the presence of low glutathione levels, allows more free radicals to damage DNA.
- Impaired Immune Function: Essential vitamins and minerals are crucial for a healthy immune system, which can be compromised by deficiencies, making the body less able to fight off cancer cells.
- Weakened DNA Repair: Many nutrients are involved in DNA repair mechanisms, and deficiencies can hinder these processes, increasing the risk of cells becoming cancerous.
Dietary Factors Associated with Lower Risk
- High intake of fruits and vegetables: These are rich in vitamins, antioxidants, and fiber, which are protective against oral cancer.
- Increased dietary fiber: Fiber helps clean and maintain a healthy digestive system and can reduce exposure to cancer-causing compounds.
খাদ্যতালিকাগত ঘাটতির সাথে মৌখিক ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি বৃদ্ধির সম্পর্ক রয়েছে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে ভিটামিন এ, সি, ডি এবং ই এর অপর্যাপ্ত গ্রহণ এবং সেলেনিয়াম, জিঙ্ক এবং আয়রনের মতো খনিজ পদার্থ গ্রহণ। এই ঘাটতিগুলি রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা দুর্বল করে দিতে পারে, ডিএনএ মেরামত ব্যাহত করতে পারে এবং অক্সিডেটিভ স্ট্রেস বাড়াতে পারে, যার ফলে কোষগুলি ক্যান্সারজনিত পরিবর্তনের জন্য আরও সংবেদনশীল হয়ে ওঠে। বিপরীতে, ফলমূল, শাকসবজি এবং খাদ্যতালিকাগত ফাইবার সমৃদ্ধ খাবার মুখের ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি হ্রাসের সাথে সম্পর্কিত।
নির্দিষ্ট ঘাটতি এবং তাদের প্রভাব
- ভিটামিন ডি: এর অভাব মৌখিক ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকির সাথে দৃঢ়ভাবে জড়িত।
- ভিটামিন এ, সি এবং ই: এই অ্যান্টিঅক্সিডেন্টগুলি ডিএনএ ক্ষতির হাত থেকে রক্ষা করে এবং মুক্ত র্যাডিকেলগুলিকে নিরপেক্ষ করে।
- লোহা: আয়রনের নিম্ন স্তরের সাথে বর্ধিত অক্সিডেটিভ স্ট্রেসের সম্পর্ক রয়েছে, যা মুখের ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি বাড়ায়।
- সেলেনিয়াম: অভাব অ্যান্টিঅক্সিডেন্ট এনজাইমের কার্যকলাপকে ব্যাহত করতে পারে, যা মুখের ক্যান্সারের বিকাশে অবদান রাখে।
- দস্তা: অভাব ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি বৃদ্ধির সাথে যুক্ত এবং কোষের বিস্তার এবং রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতার কার্যকারিতায় ভূমিকা পালন করে।
- গ্লুটাথিয়ন (GSH): নিম্ন স্তরের সাথে অক্সিডেটিভ স্ট্রেস বৃদ্ধি এবং মুখের ক্যান্সারের ঝুঁকি বেশি থাকে।
ঘাটতি কীভাবে ক্যান্সারে অবদান রাখে
- জারণ চাপ: ভিটামিন এ, সি এবং ই এর মতো অ্যান্টিঅক্সিডেন্টের অভাব এবং গ্লুটাথিয়নের মাত্রা কম থাকার কারণে, আরও বেশি ফ্রি র্যাডিকেল ডিএনএর ক্ষতি করতে পারে।
- প্রতিবন্ধী রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতা: সুস্থ রোগ প্রতিরোধ ক্ষমতার জন্য অপরিহার্য ভিটামিন এবং খনিজ পদার্থ অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ, যা ঘাটতির কারণে ক্ষতিগ্রস্ত হতে পারে, যার ফলে শরীর ক্যান্সার কোষের বিরুদ্ধে লড়াই করতে কম সক্ষম হয়।
- দুর্বল ডিএনএ মেরামত: অনেক পুষ্টি উপাদান ডিএনএ মেরামত প্রক্রিয়ার সাথে জড়িত, এবং এর ঘাটতি এই প্রক্রিয়াগুলিকে বাধাগ্রস্ত করতে পারে, কোষগুলির ক্যান্সারে পরিণত হওয়ার ঝুঁকি বাড়ায়।
ঝুঁকি কমানোর সাথে সম্পর্কিত খাদ্যতালিকাগত কারণগুলি
- ফলমূল ও শাকসবজি বেশি পরিমাণে গ্রহণ: এগুলিতে প্রচুর পরিমাণে ভিটামিন, অ্যান্টিঅক্সিডেন্ট এবং ফাইবার রয়েছে, যা মুখের ক্যান্সারের বিরুদ্ধে প্রতিরক্ষামূলক।
- খাদ্যতালিকায় আঁশের পরিমাণ বৃদ্ধি: ফাইবার একটি সুস্থ পাচনতন্ত্র পরিষ্কার এবং বজায় রাখতে সাহায্য করে এবং ক্যান্সার সৃষ্টিকারী যৌগের সংস্পর্শ কমাতে পারে।
How Betel quid causes oral cancer?
Betel quid causes oral cancer through a combination of chemical and mechanical irritation that leads to DNA damage, chronic inflammation, and the development of precancerous lesions. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies areca nut, the key ingredient in betel quid, as carcinogenic to humans. The risk increases with the frequency and duration of chewing, and is further compounded if tobacco is also used.
Chemical and toxic effects
The cancer-causing potential of betel quid is driven by several key components:
- Areca nut: Contains alkaloids such as arecoline, which is a Group 1 carcinogen. These compounds are absorbed through the oral mucosa and lead to the formation of carcinogenic nitrosamines, which can directly cause genetic mutations.
- Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide): The alkaline lime in the quid speeds up the release of arecoline and is highly corrosive to the oral tissues. In combination with areca nut compounds, it generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause oxidative damage to the DNA of oral cells.
- Tobacco: When added to the quid, tobacco acts synergistically with the other ingredients, significantly increasing the risk of oral cancer. Studies have shown that chewers who combine betel quid with tobacco face a much higher risk than those who chew without it.
Physical and mechanical irritation
The chewing process itself physically damages the oral tissues and facilitates the absorption of harmful chemicals:
- Abrasive fibers: The crude fibers in the areca nut cause constant friction and microtrauma to the delicate lining of the mouth. This repeated physical injury creates pathways for the chemical irritants and carcinogens to penetrate deeper into the submucosal tissue.
- Chronic inflammation: The combined chemical and mechanical insults trigger a chronic inflammatory response in the oral mucosa. Prolonged inflammation is a key driver of cancer, as it promotes cell proliferation, genetic mutations, and other cellular changes.
Development of precancerous conditions
The long-term effects of chewing lead to potentially malignant disorders that can progress into full-blown cancer. These include:
- Oral submucous fibrosis (OSF): A major precursor lesion caused by betel quid. The chronic inflammation and stimulation of fibroblasts lead to a buildup of collagen and stiffening of the oral tissues. This results in reduced mouth opening (trismus) and increases the risk of malignant transformation. The rate of malignant transformation for OSF is estimated to be between 1.99% and 7.6% over a 10-year period.
- Oral leukoplakia: The development of white patches on the oral mucosa, another common precancerous lesion among betel quid chewers. Certain types of leukoplakia have a higher potential for malignant transformation.
Cellular and genetic changes
At the cellular level, betel quid use drives carcinogenesis through multiple mechanisms:
- DNA damage: The alkaloids and reactive oxygen species cause mutations in crucial genes that regulate cell growth, such as the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. These mutations allow cells to grow uncontrollably and become cancerous.
- Gene methylation: The chemicals can alter DNA methylation patterns, including hypermethylation of tumor-suppressor genes like DUSP4, which can be a specific marker for betel quid-related oral cancer.
- Altered microbiome: Betel quid chewing changes the balance of bacteria in the mouth. Some studies have linked these microbial shifts to the progression of precancerous lesions, though further research is needed to understand the exact mechanisms.
